一图胜千言
1 - Gitignore 规则总结
Gitignore 文件用于指定 Git 应该忽略哪些文件和目录,不将它们纳入版本控制。
放置位置
- 项目根目录: 规则适用于整个仓库。
- 子目录: 规则适用于该子目录及其所有子目录。
规则语法
- 空行或以
#开头的行:被视为注释,会被忽略。# 这是一个注释 - 标准 glob 模式匹配:
*:匹配零个或多个字符。?:匹配一个任意字符。[]:匹配括号中任意一个字符。
- 匹配目录:在模式末尾添加斜杠
/来指定只匹配目录。temp/ # 忽略名为 temp 的目录及其所有内容 - 排除模式(否定):在模式前加
!来取消忽略。如果一个文件被前面的规则忽略了,但又被排除模式匹配,它将不被忽略。*.log # 忽略所有 .log 文件 !important.log # 但不忽略 important.log - 开头斜杠
/:将模式锚定到.gitignore文件所在的目录。如果.gitignore在项目根目录,则锚定到项目根目录。/build # 只忽略项目根目录下的 build 目录,不忽略 src/build - 双星号
**:**/:匹配任意深度的文件或目录。**/logs忽略任意目录下的logs目录。pattern/**:匹配指定目录下的所有文件和子目录。docs/**忽略docs目录下的所有文件和子目录。a/**/b:匹配a目录下的任意深度的b文件或目录。例如,a/b,a/x/b,a/x/y/b。
匹配顺序与优先级
- 后来居上:
.gitignore文件中后出现的规则会覆盖先出现的规则。 - 层级优先: 子目录中的
.gitignore文件中的规则会覆盖父目录中的.gitignore文件中的规则。 - 否定规则: 否定模式 (
!) 重新包含先前被忽略的文件。被!规则重新包含的文件不会再被同一个.gitignore文件中后续的规则排除。
注意事项
- 已跟踪文件: 一旦文件已经被 Git 跟踪(即已经提交过),
.gitignore规则将不再对其生效。你需要使用git rm --cached <file>命令从 Git 索引中移除该文件,然后 Git 才会开始忽略它。
示例
# 忽略所有 .log 文件
*.log
# 忽略根目录下的 build 目录
/build
# 忽略 node_modules 目录及其内容
node_modules/
# 忽略所有 temp 目录,无论深浅
**/temp/
# 忽略所有 .txt 文件,但保留 important.txt
*.txt
!important.txt
2 - Git
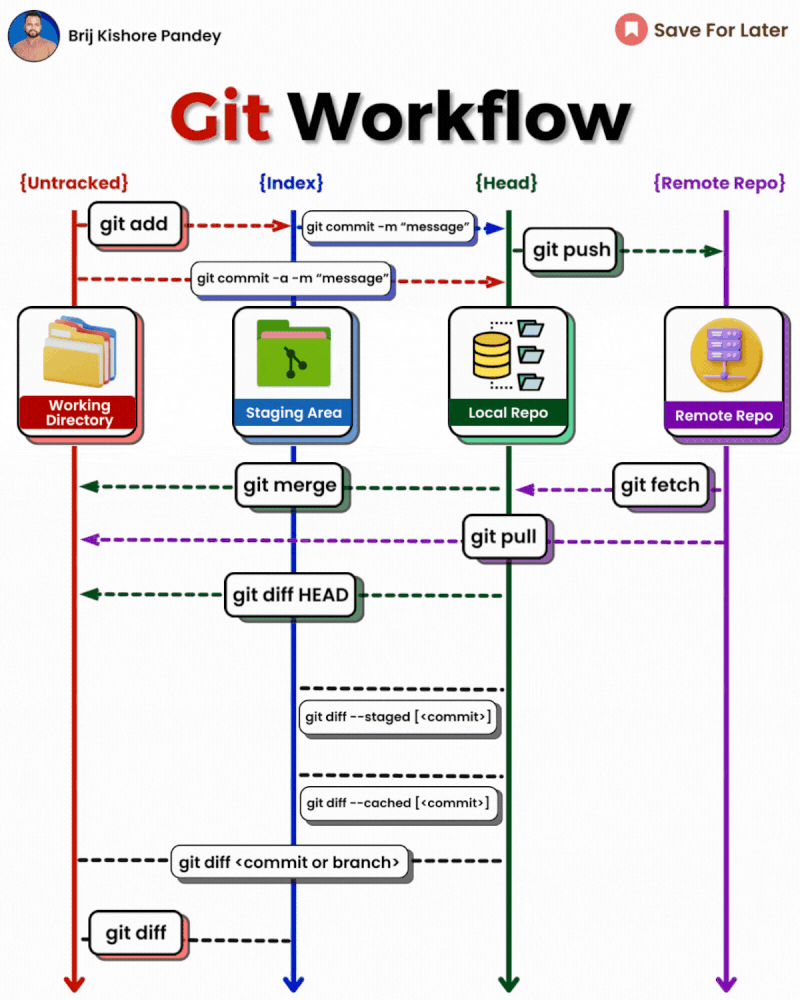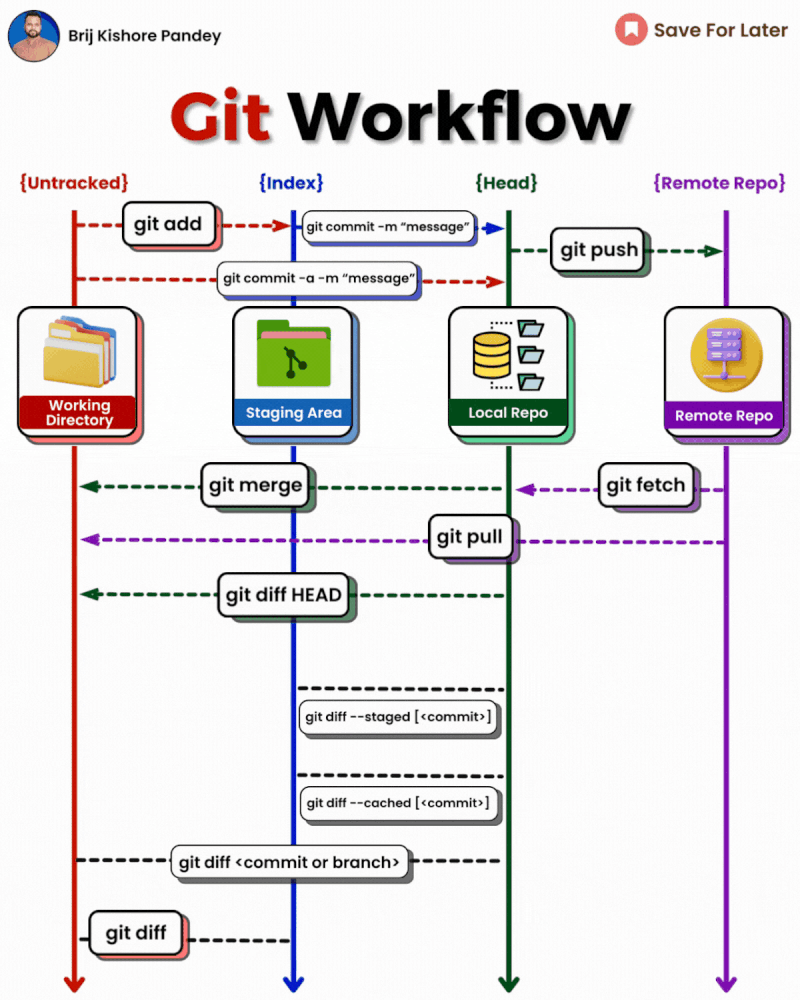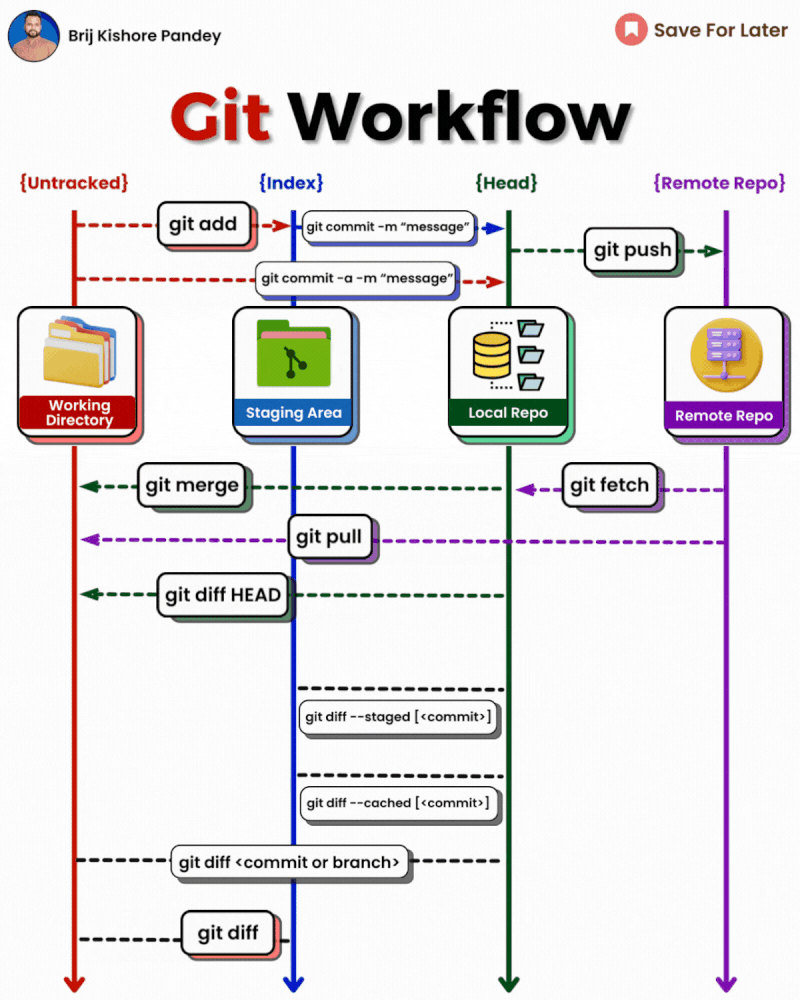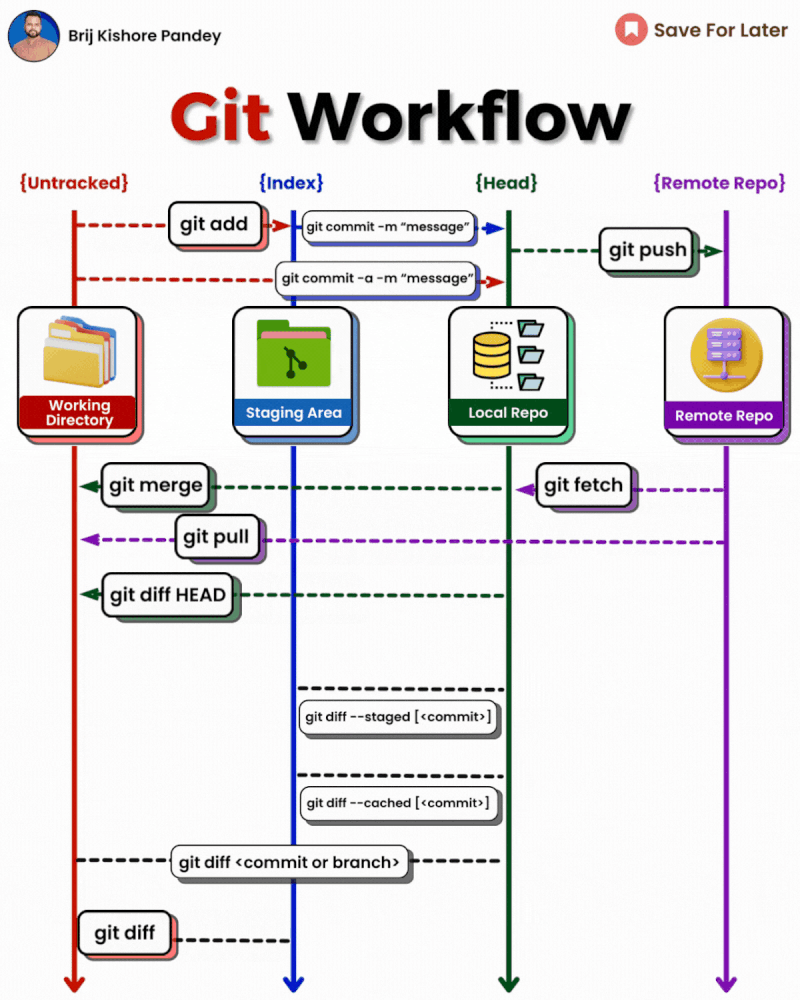
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗱𝗶𝗳𝗳: Show file differences not yet staged.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁-𝗮 -𝗺 "𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁 𝗺𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗮𝗴𝗲": Commit all tracked changes with a message.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝘀𝘁𝗮𝘁𝘂𝘀: Show the state of your working directory.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗮𝗱𝗱𝗳𝗶𝗹𝗲_𝗽𝗮𝘁𝗵:Add file(s) to the staging area.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗵𝗲𝗰𝗸𝗼𝘂𝘁-𝗯 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵_𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗲: Create and switch to a new branch.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗵𝗲𝗰𝗸𝗼𝘂𝘁𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵_𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗲: Switch to an existing branch.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁–𝗮𝗺𝗲𝗻𝗱:Modify the last commit.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗽𝘂𝘀𝗵𝗼𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵_𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗲: Push a branch to a remote.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗽𝘂𝗹𝗹: Fetch and merge remote changes.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝗯𝗮𝘀𝗲-𝗶: Rebase interactively, rewrite commit history.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗹𝗼𝗻𝗲: Create a local copy of a remote repo.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗺𝗲𝗿𝗴𝗲: Merge branches together.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗹𝗼𝗴–𝘀𝘁𝗮𝘁: Show commit logs with stats.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝘀𝘁𝗮𝘀𝗵: Stash changes for later.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝘀𝘁𝗮𝘀𝗵𝗽𝗼𝗽: Apply and remove stashed changes.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝘀𝗵𝗼𝘄𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁_𝗶𝗱: Show details about a commit.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝘀𝗲𝘁𝗛𝗘𝗔𝗗~𝟭: Undo the last commit, preserving changes locally.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗮𝘁-𝗽𝗮𝘁𝗰𝗵 -𝟭 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁_𝗶𝗱: Create a patch file for a specific commit.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗮𝗽𝗽𝗹𝘆𝗽𝗮𝘁𝗰𝗵_𝗳𝗶𝗹𝗲_𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗲: Apply changes from a patch file.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵-𝗗 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵_𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗲: Delete a branch forcefully.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝘀𝗲𝘁: Undo commits by moving branch reference.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘁: Undo commits by creating a new commit.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗵𝗲𝗿𝗿𝘆-𝗽𝗶𝗰𝗸 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁_𝗶𝗱: Apply changes from a specific commit.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵: Lists branches.𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝘀𝗲𝘁 --𝗵𝗮𝗿𝗱: Resets everything to a previous commit, erasing all uncommitted changes
小技巧
在所有提交中查找某个关键字:
git grep "近亲" $(git rev-list --all .)3 - Latency Numbers Every Programmer Should Know
在线预览地址:Latency Numbers Every Programmer Should Know
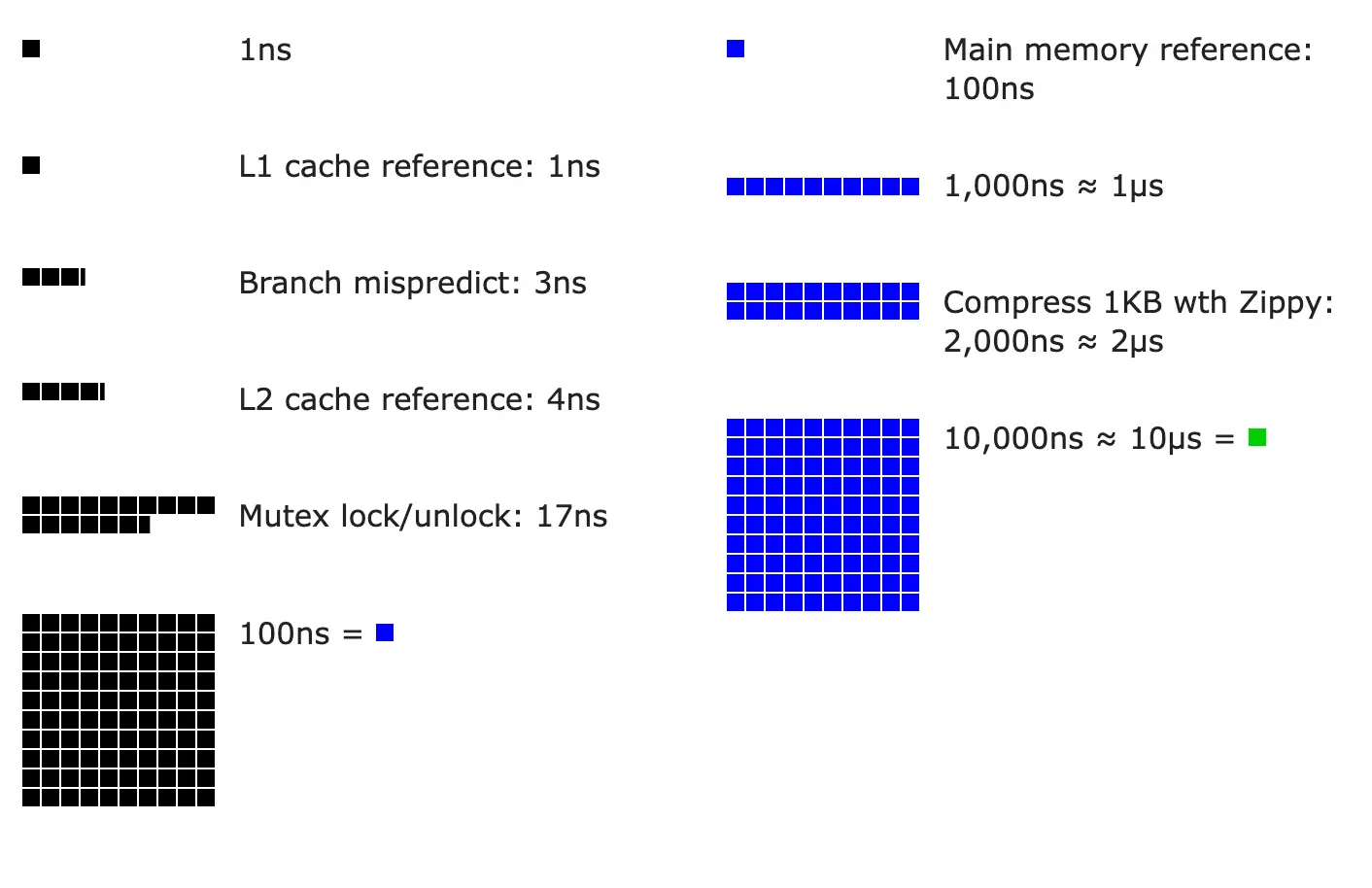

From Google SRE book
| Operation | Time in ns | Time in ms (1ms = 1,000,000 ns) |
|---|---|---|
| L1 cache reference | 1 | |
| Branch misprediction | 3 | |
| L2 cache reference | 4 | |
| Mutex lock/unlock | 17 | |
| Main memory reference | 100 | |
| Compress 1 kB with Zippy | 2,000 | 0.002 |
| Read 1 MB sequentially from memory | 10,000 | 0.010 |
| Send 2 kB over 10 Gbps network | 1,600 | 0.0016 |
| SSD 4kB Random Read | 20,000 | 0.020 |
| Read 1 MB sequentially from SSD | 1,000,000 | 1 |
| Round trip within same datacenter | 500,000 | 0.5 |
| Read 1 MB sequentially from disk | 5,000,000 | 5 |
| Read 1 MB sequentially from 1Gbps network | 10,000,000 | 10 |
| Disk seek | 10,000,000 | 10 |
| TCP packet round trip between continents | 150,000,000 | 150 |
Therefore, it is possible to read:
- sequentially from HDD at a rate of ~200MB per second
- sequentially from SSD at a rate of ~1 GB per second
- sequentially from main memory at a rate of ~100GB per second (burst rate)
- sequentially from 10Gbps Ethernet at a rate of ~1000MB per second
Back of the Envelope Calculations
Quick tips: Use numbers based on the decimal system to run numbers in your head. Sample calculation:
- What is the overall latency of retrieving 30 256kB images from one server?
Naïve design: do all the work on one machine - dominated by disk seek time.
| Reads required to generate page | 30 images / 2 disks per machine = 15 |
| Time to read one image from HDD | (256KB / 1MB) * 5 ms + 10 ms seek = 11.28 ms |
| Approximate time to generate results | 15 reads * 11.28 ms = 169.2 ms |
One HDD-based server can generate 1000 ms / 169.2 ms ~= 5 result pages per second.
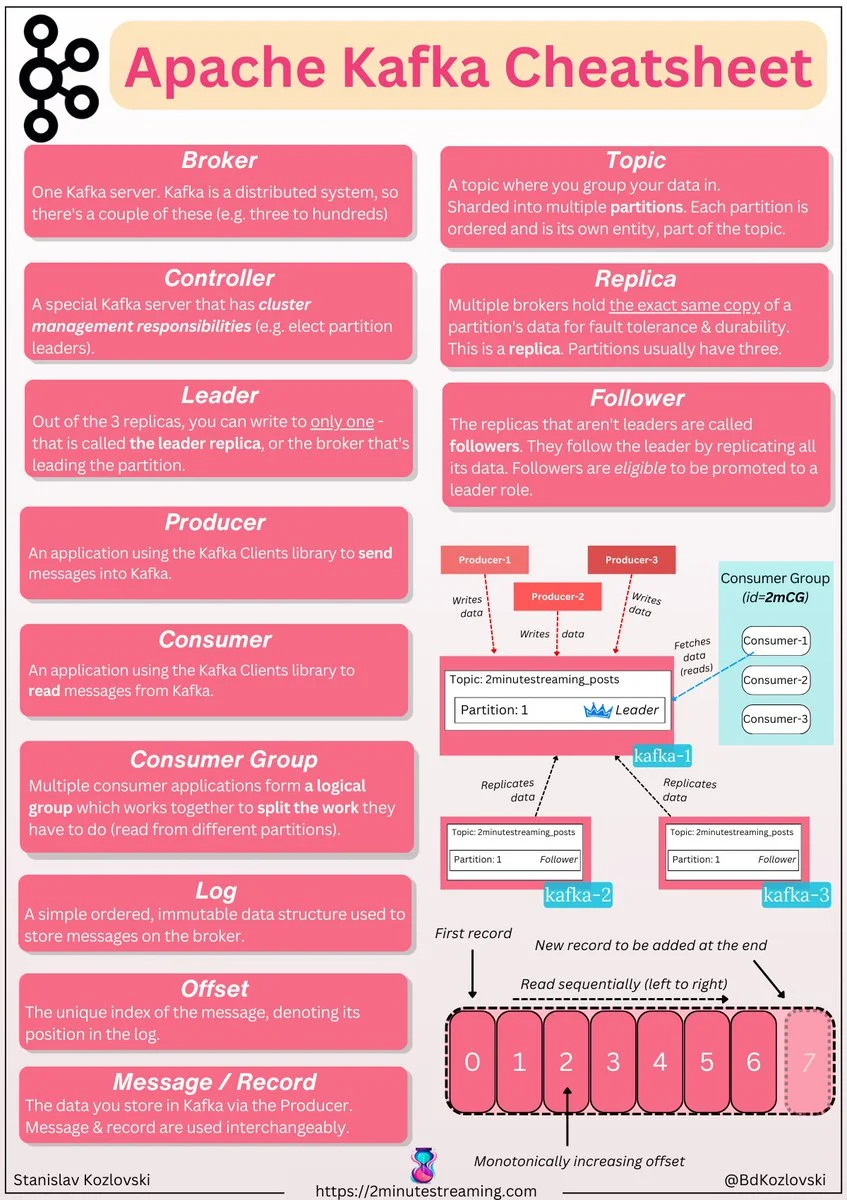
4 - Kafka
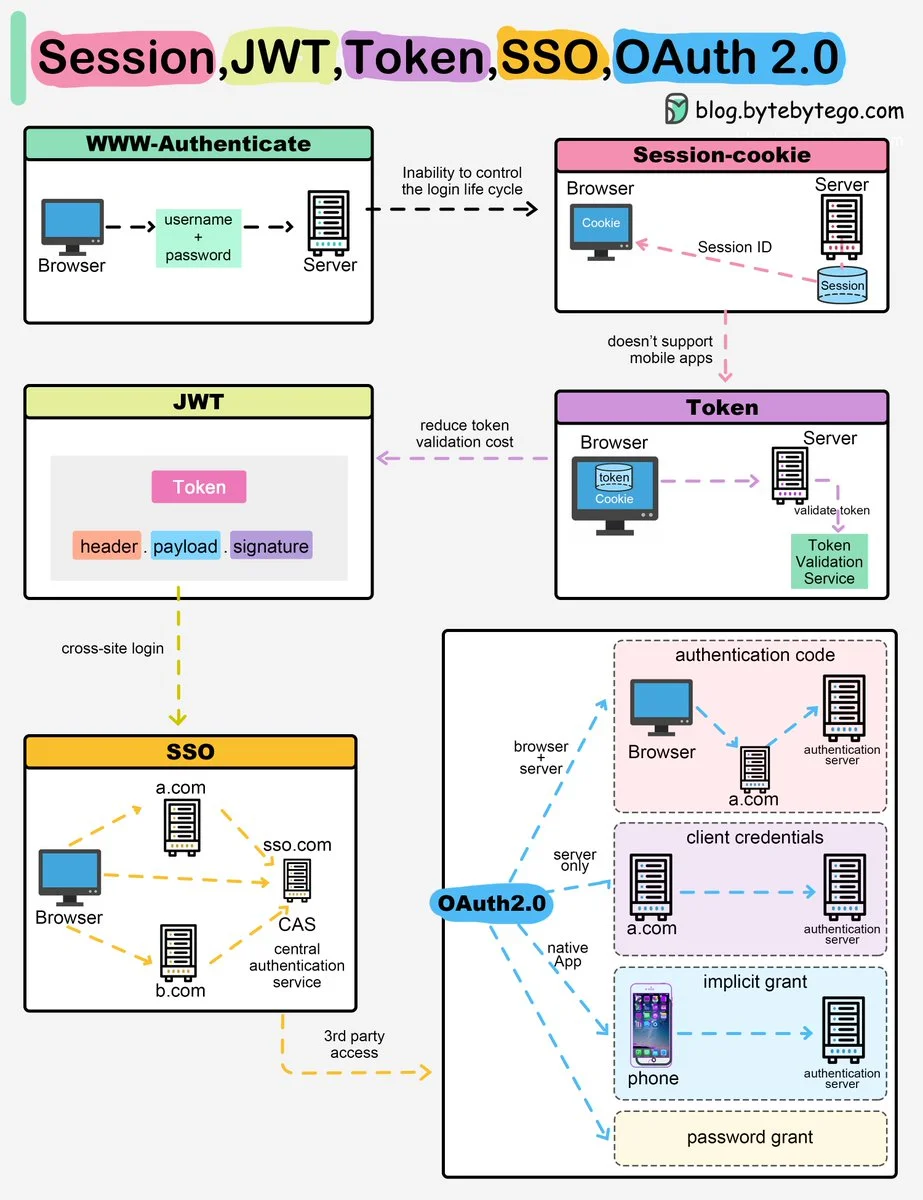
5 - Web authorization
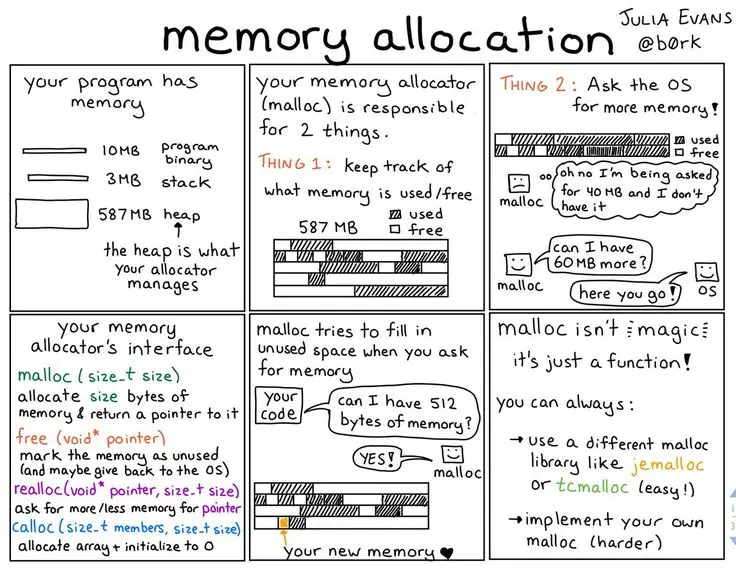
6 - Memory allocation